How To Change Front Control Arm Bushings On Bmw E46
Suspension Nuts for BMW ane/2/3/four-series Models, including M Models
This folio applies to BMW models: E82, F22, F87, E36, E46, E90, E92, E93, F30, F31, F36, G20, F80, F32, F33, F34, G22, F82, F83, E85, E86
Scratching your head on BMW break types, options, and opinions? We all were at one point. This page is a "Suspension 101" introduction to interruption layouts, terminology, and types for BMW enthusiasts. You lot won't find our recommendations here (see links at the bottom) as this page exists to educate and inform. Well-nigh the bottom you volition observe a "Pictionary" style glossary of BMW suspension components.
Information technology's incommunicable to encompass all types of BMW suspensions on a single spider web page. Books devote whole capacity to each model. We're going to cover the basics in a very generalized style to get yous acquainted with BMW suspensions. Our focus volition mainly be on 1992-2005 BMW iii-serial and 2006+ one/2/three/4-series models.
What you lot will notice well-nigh is that rubber bushings are everywhere in a BMW suspension. Some use a hybrid fluid and rubber bushing design chosen a hydrobearing. Prophylactic is an excellent pick for a suspension bushing - if you're selling millions of cars. It's cheap, like shooting fish in a barrel to produce, comfortable, reacts rapidly, resistant to chemicals and moisture, requires no maintenance, can be fabricated in whatsoever shape, and the rubber chemical compound can exist tailored for each application. The BMW ride and handling is and then often historic considering of the safety bushings in the suspension but information technology'south a compromise. The intermission tuning must alive upwardly to the "Ultimate Driving Machine" reputation just also appeal to a ever-increasing consumer audience. Consequently the bushings and suspensions have gotten softer. One complaint nosotros oft hear is that BMWs have become as well soft but that's the trade-off BMW fabricated to sell more cars. Besides, it'southward easy to change a bushing to brand the motorcar more responsive and sportier.
1992-2006 3-series, 2003-2008 Z4
E36 (except 318ti), E46 iii-series, including M3 models, E85/E86 Z4)
The front end suspension was basically carried over from the E30 three-series models, using a single boomerang-shaped command arm and MacPherson strut. The rear changed from a simple trailing arm per side to a more than complex "Z-link" rear pause anchored past a big semi-trailing arm and upper and lower link per side. Trivia fact: this rear pause was originally developed on the Z1 roadster.
Front end Break

BMW Single Pivot front end suspension on E30, E36, E46, Z3, & Z4.
(image shows early version of E46 front control arm)
Strut: MacPherson design, "coil over" spring on the strut housing with a large upper rubber-isolated mountain. The strut associates (strut + spring) is bolted or clamped to the spindle. Springs do not typically wearable or sag but the strut volition go worn out and no longer hold pressure. The strut tin can exist replaced but the entire assembly must be taken autonomously. Ever get new mounts, bump stops, and spring pads. Reinforcement plates exist for the sheetmetal where the strut is mounted and they are strongly recommended.
Control Arm: often called a wishbone in BMW parts diagrams but looks more than similar a boomerang. It contains 2 ball joints: an outer at the spindle and an inner attached through the front subframe. A rubber bushing locates the arm to the frame rail. Brawl joints article of clothing quickly and tin exist a condom concern. The rubber bushings go too soft, leaving the steering and treatment mushy and no longer as precise as it used to be.
Sway Bar: located nether the front frame rails and engine bay with rubber bushings. The ends are attached either to the control arms or to the strut housing. The links contain ball joints that are a known source for rattles and clunks.
Rear Suspension

BMW Key C-link rear suspension on E36, E46, E85, and E89 (internal lawmaking HA3).
Shock: a unmarried shock on each side is bolted to the spindle at the bottom and through the body with a rubber mount at the pinnacle. Shocks typically concluding a long time only tin can wear out and no longer hold pressure. Unlike the front strut, the stupor can be replaced on its own with minimal disassembly. The shock mount, on the other paw, is a very mutual failure signal and may need to be replaced before the shock wears out. There are several shock mount upgrades that last longer. Reinforcement plates be for the sheetmetal where the shock is mounted and they are strongly recommended.
Subframe: the entire rear suspension and differential, autonomously from the shock, is anchored by a steel subframe bolted to the trunk floor. The flooring area itself is weak and cracks in the sheetmetal are common. Reinforcement plates exist for the sheetmetal and they are strongly recommended.
Semi-Trailing Arm: the other major component in the rear suspension. The semi-abaft arm, or merely trailing arm, provides the outer mounting betoken for the axle shaft, upper and lower command artillery, shock absorber, every bit well as the brake assembly. It'southward mounted at the front end using a safe bushing recessed into a pocket in the chassis (under the rear seat). The back of the trailing arm contains upper and lower bushings (or sealed bearings) and the axle. The forward bushings are common wear items leading to loose or "squirrely" handling. The rear upper and lower bushings are either condom and will vesture out or a innovative sealed ball joint that lasts a long time. The seal ball joint can exist used as an upgrade over its rubber counterpart.
Upper Control Arm: used to locate the leap. It attaches to the subframe on the inside with a rubber bushing and to the trailing arm with a sealed ball articulation.
Lower Control Arm: also called a wishbone past BMW (quite accurate) or the camber arm equally information technology's used to set the camber alignment on the rear. Besides mounted with a rubber bushing on the within or a safety bushing or sealed ball joint on the exterior. These arms are fabricated from sparse steel and are designed to bend easily to prevent damage to the rest of the suspension. If yous take trouble getting the alignment in spec or the car sits differently on one side, it could be from a bent lower arm. It's also common to supercede this with a fully-adjustable arm to gain more than negative rear camber.
Sway Bar: runs around the dorsum of the subframe and differential, mounted with rubber bushings, with links attaching the bar ends to the upper control arm.
2006-current 1/2/3/4-serial
E82 1-series, F22 ii-series, E9X iii-serial, F30 3-series, G20 3-serial, F32 4-series, G22 4-series, including 1M/M2/M3/M4 models, G29 Z4
A massive modify to the interruption layout occurred for the 2006 model year. The E90 iii-series adopted the same intermission design as 5/6/7-series models, although no parts are shared. The front at present used two command arms per side forth with a MacPherson strut. The rear dropped the massive semi-trailing arm in favor of multiple smaller arms still attached to the rear subframe. The pause layout is still in utilise today on the very latest G20 3-series and G22 4-serial models (although parts are not interchangeable).
Front Suspension

BMW Double Pin front suspension.
Strut: MacPherson design, "coil over" jump on the strut housing with a large upper prophylactic-isolated mount. The strut assembly (strut + spring) is clamped to the spindle. Springs do not typically wear or sag only the strut will become worn out and no longer hold pressure. The strut can be replaced but the entire associates must be taken apart. Ever get new mounts, bump stops, and leap pads.
Upper Control Arm (aka Thrust Arm or Tension Strut): this arm is mounted ahead of the lower arm, and the outer ball articulation points downward. The arm is not straight and has several bends in its shape. The dual front control arms practice a better job of controlling wheel motions during cornering and when the intermission compresses. The upper arm absorbs most of the impacts and vibrations equally the break moves. The inner bushing tin can be a weak point as it's filled with a dampening fluid that can leak or evaporate. With no forcefulness in the bushing the ride and treatment quickly deteriorate. At that place's no mode to refill the fluid then the consummate bushing needs to exist replaced. The M2/M3/M4 models use a not-hydro bushing that can exist used equally an upgrade.
Lower Command Arm (aka Wishbone): this arm sticks straight out from the front subframe. The arm itself is straight simply will take a slight upward bend. The outer ball articulation points up. The arm'due south principle purpose is to command camber alter equally the pause compresses. Information technology has a sealed inner ball joint that almost never wears out.
Sway Bar: located under the front end frame runway and engine bay with rubber bushings. The ends are attached either to the control arms or to the strut housing. The links contain ball joints that are a known source for rattles and clunks.
Rear Suspension

BMW 5-link rear suspension (internal code HA5).
Stupor: a single daze on each side is bolted to the lower arm and through the trunk with a condom mount at the elevation. Shocks typically last a long time but can wear out and no longer hold pressure. Unlike the forepart strut, the stupor can be replaced on its own with minimal disassembly.
Subframe: the entire rear suspension and differential, apart from the daze, is anchored by a steel subframe bolted to the trunk flooring. Unlike the previous designs, there are no issues with the rear flooring cracking. The subframe mounts are a soft-ish prophylactic compound that are oftentimes replaced with a urethane or aluminum mount that does non flex as much.
Control Arms: this break uses 5 (5) rear control arms. More arms means the suspension movement and load is spread over a larger area, which ways less habiliment and tear and amend control. There is no longer a cardinal semi-trailing arm but at that place is a chief arm that BMW calls a "ringlet-over strut". The shock and spring are both located on this lower arm. All of the arms are mounted to the spindle and to the subframe using rubber bushings. The M2/M3/M4 models use the sealed ball joint design and most of those artillery can be used to upgrade the non-Thousand models. This is specially important on high-horsepower tuned turbo models where the original rubber bushings let too much twist, deflection, and axle hop during acceleration.
Sway Bar: located over the subframe with safety bushings. The ends are attached to the "roll-over strut" lower control arm. The placement of the bar on top of the subframe makes it challenging to remove for an upgrade just it tin exist washed while doing other related work.
A Pictorial Glossary of BMW Suspension Terms (a "Pictionary")
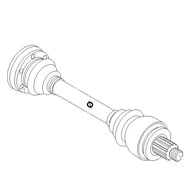 Axle | Part of the driveline. Information technology'southward a shaft extending from the differential to the spindle and hub. They are more commonly known as half-shafts or axle-shafts. The "axle" may besides refer to the consummate front end or rear break, encompassing the shocks, control arms, bushings, sway bar, one-half-shafts, spindle, and even inclusive of the brakes. |
 Ball Joint | An internal intermission component consisting of the a steel brawl encased in a metal, plastic, or rubber isolated cup and with a threaded stud for mounting. The ball is able to rotate inside the cup and let the interruption component to change management. Brawl joints are typically mounted to permit horizontal movement (side to side). They are a common wear detail as the internal plastic or safe isolator breaks downwardly and can no longer comprise the ball. |
 Bushing | Typically a formed condom piece used to locate a component to another component. The sway bar is mounted to the body using a safety block. Rubber is a favorite textile (come across paragraph above) only is oft replaced with a stiffer rubber compound, urethane, Delrin, or even equally rotating bearing. |
 Camber | The angle of the tire in relation to a apartment World. BMWs accept slight negative slant as a baseline - the top of the tire tilts inward. Every bit the motorcar corners the exterior tire will spread flatter to the pavement, increasing its contact patch. It'southward common to add together more negative camber to get more grip on the race track. Too much negative camber causes the tire to ride on its inside shoulder when going straight. |
 Camber Arm | A rear pause component designed to command and/or adapt slant. On the E36/E46/Z4 it'due south the rear lower wishbone. It'south fabricated of sheetmetal and bends easily. It'south designed to curve so that in an impact the arm takes all the free energy and something else isn't damaged. If yous notice one side of the rear is a different camber or ride height check the lower slant arm. |
 Camber Plate | A front suspension component designed to control and/or adjust slant. The slant plate often replaces the upper strut mount. More negative camber is desired for runway use to improve front end grip and reduce understeer. Lowered cars oft need the negative slant reduced to right for tire habiliment. So not all camber plates are the same. |
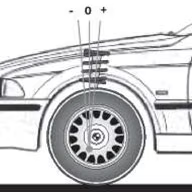 Pulley | The rearward tilt of the front steering axis centerline, measured in degrees. The Caster is the degrees between a vertical line drawn directly up from the steering pin point and the bending of the strut. BMWs have not-adaptable positive caster where the strut is angled backwards towards the driver. This increases stability at high speeds. Too much volition make steering try higher. |
 Curlicue-Over | A shock absorber with the spring mounted effectually the trunk of the shock. A MacPherson strut is technically a gyre over. In the parts world, the term is reserved for performance shock and spring packages that accept a threaded spring perch to allow ride height adjustments. |
 Command Arm | A suspension component designed to maintain the desired pause alignment during suspension motility. It will also absorb vibrations and impacts with a bushing. Multiple control arms will exercise a better job of controlling alignment. |
 Damper | Another give-and-take for shock absorber or strut. Damper is a catch-all term that tin can apply to a front strut or rear stupor. The damper's purpose is to command the motion of the bound and the balance of the suspension. The shock must be soft plenty in compression to provide a comfortable ride merely stiff enough in extension to continue the pause from oscillating and keep the tire planted on the ground. |
 Hub | A solid surface for mounting the wheel. It'southward frequently used as a reference for the zipper of other components - "the strut is mounted to the hub". Used interchangeably with the spindle. |
 Hydrobearing | A safe bushing that holds a thick dampening fluid to help absorb vibrations. Unfortunately, when the fluid is gone the remaining rubber bushing cannot properly dampen the vibration or control suspension move. A clunk, rattle, or vibration will exist felt. Fluid is a swell damper of vibration but the bushing is not serviceable and information technology'southward easy for the fluid to leak or evaporate. Solid rubber or urethane are splendid alternatives. |
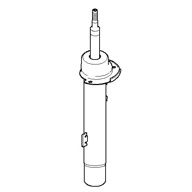 MacPherson Strut | A strut/damper blueprint that acts equally another link in the forepart suspension. This is different than a upper and lower control arm layout with a shock mounted independently from the arms. With a MacPherson design, the strut is an disquisitional slice in the intermission associates. With the strut mounted directly to the spindle the internal damper moves at most 1:i ratio to the wheel. All BMW one/2/3/4-series models use a MacPherson front strut. |
 Multi-Link | A catch-all term for any interruption that has multiple control arms and attachment points to the chassis. The E9X rear break is known equally a 5-link layout. |
 Radius Arm | Another BMW term for a control arm. It's almost often used on front end upper control arms. |
 Reinforcement | A piece of sheetmetal, shaped to match the design and shape of an existing sheetmetal body piece that volition add force and rigidity. Unfortunately, some BMW models require extra reinforcement in suspension locations. |
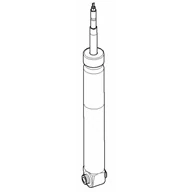 Shock | A rear suspension damper that slows and controls the scroll spring. See "Damper" in a higher place. A shock differs from a strut because the it is not an integral part of the suspension. The control arms, spring, and hub could role without a shock (only you wouldn't want them to). |
 Stupor Mount (RSM) | A rubber bushing used to mount the rear shock absorber to the chassis. |
 Spindle | A central mounting signal for multiple suspension components, including the outer control arms and the lower strut mount. It also provides a mounting bespeak for the cycle bearing, hub, and brakes. |
 Spring | All BMWs apply either a steel coil jump or an airbag. Springs come in different lengths and rates, depending on the model and included options. Ride stiffness nearly oft comes from the spring rate then it's very easy to become besides stiff and make the rest of the suspension ineffective. Too stiff and too soft will both negatively bear on tire grip and handling just in that location is e'er a sweet spot. |
 Strut | A forepart suspension damper that slows and controls the roll spring. See "Damper" higher up. A "strut" differs from a shock because it carries the spring and has some load-bearing part. |
 Strut Mount | A rubber bushing encased in steel or aluminum used to mountain the front strut to the chassis. |
 Subframe | A big steel or tubular structure bolted to the motorcar's chassis and used to locate the rest of the command arms. The front too provides a mounting point for the engine mounts. The rear is likewise the mounting point for the differential and axle-shafts. |
 Subframe Mount | A dumbo condom mountain pressed into the subframe that provides isolation for the subframe, differential, and command arms. |
 Sway Bar (Anti-Roll Bar) | A solid steel bar that counteracts the intermission motion during cornering. It acts as a lever - twisting equally the interruption compresses. Every bit one side compresses the bar twists to force the contrary tire to the pavement. The bar is mounted to the body of the automobile with rubber bushings |
 Sway Bar Link | The sway bar is fastened to the break with a small arm called the link. A ball articulation is located on each end and allows the link to rotate and motion freely equally the sway bar moves. |
 Tension Strut | Another BMW term for a control arm. It'southward most often used on forepart upper command arms. |
 Thrust Arm | Some other BMW term for a control arm. It's near frequently used on front upper control arms. |
 Toe | An alignment spec for the angle of the tire in relation to the centerline of the car. Toe is measured at the front/leading border of the tire on the same axle. If the tires are pointing away from each other the toe is "out". When the tires point in towards each other, the toe is "in". Forepart toe adjustment is done via the necktie rod. Rear toe is sometimes adjusted from either the trailing arm or a dedicated toe control arm. |
 Trailing Arm | The primary command arm in the rear interruption. Information technology's actually a semi-abaft arm considering it's forward mounting point is ahead of the rear subframe. Just information technology'due south shortened to trailing arm. On E36/E46 it'south a huge steel piece and includes the rear spindle and hub. On later cars it's now much smaller and the spindle is split up. |
 Cycle Bearing | A bearing used at each hub and allows the wheel and restriction rotor to spin. The begetting is frequently pressed into the hub, which is then bolted or pressed to the spindle. |
 Wishbone | Another term for a control arm. It'southward used on the front every bit the "lower command arm" and on the rear in multiple points. Information technology's a wishbone because it has three mounting surfaces - 1 at an finish and two at the opposing finish. |
Read more than...
one. BMW Street Suspensions - our recommendations for suspensions used exclusively on the street (click here).
Source: https://www.bimmerworld.com/About-Us/BMW-Suspension-Basics/
Posted by: shepherdfrocution.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Change Front Control Arm Bushings On Bmw E46"
Post a Comment